Circular Design Principles in Interior Design and Why They Matter
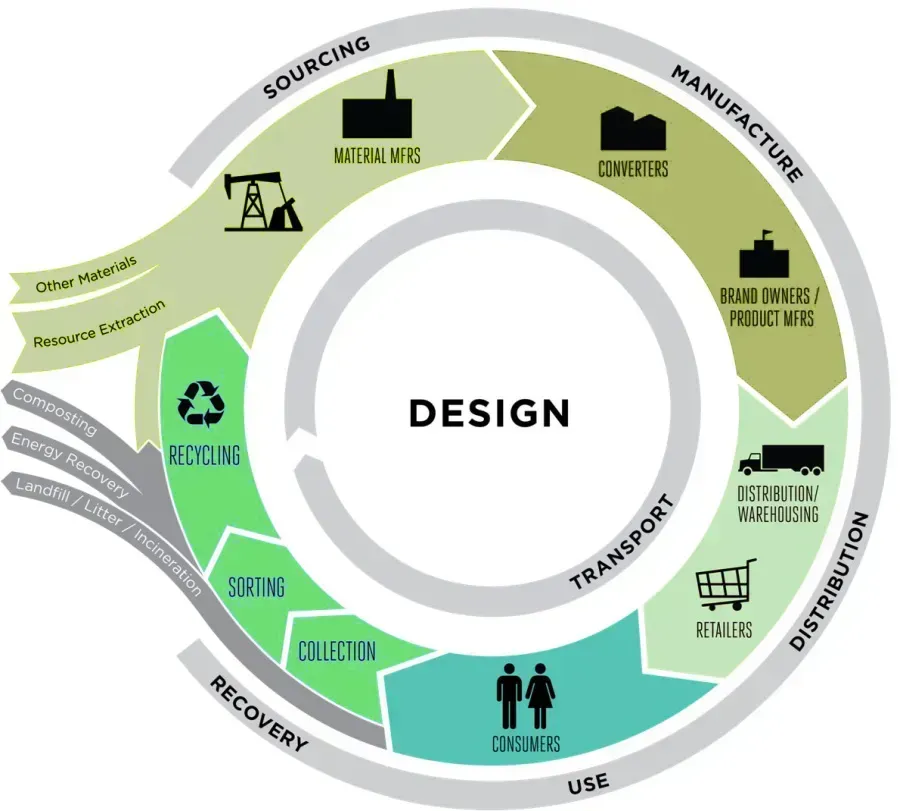
Circular design is a sustainable approach to design that considers an entire project at conception, from beginning to end and beyond, to minimize waste and maximize the conscious use of resources and products by creating systems that are regenerative and restorative by intention.
It is grounded in the principles of the circular economy, which contrasts with the traditional “take-make-waste” linear model of production and consumption. Instead, it emphasizes reusing, repurposing, recycling, repairing, and regenerating materials and products to extend their lifecycle.
The product life cycle. Source: medium.com
Core Principles of Circular Design:
- Design out waste and pollution
This can be achieved by designing products and processes that are more efficient, consume fewer resources, and generate less waste throughout their lifecycle. By extending the lifespan of products, we reduce the need for constant replacement, thereby diminishing waste generation and conserving valuable resources.
- Keep products and materials in use
To facilitate the efficient reuse or recycling of materials, the closed-loop design encourages the creation of products that can be easily taken apart. By designing products for disassembly, we enable their components to be repurposed or recycled, further reducing waste and promoting closed-loop systems.
- Regenerate natural systems
Moving to a regenerative system allows us to emulate natural systems. Based closely on the principles of nature, circular design follows the examples found in natural ecosystems, where waste is continuously repurposed or transformed into new valuable resources, creating a closed-loop system. By keeping products and materials in use, less land is required for sourcing raw virgin materials

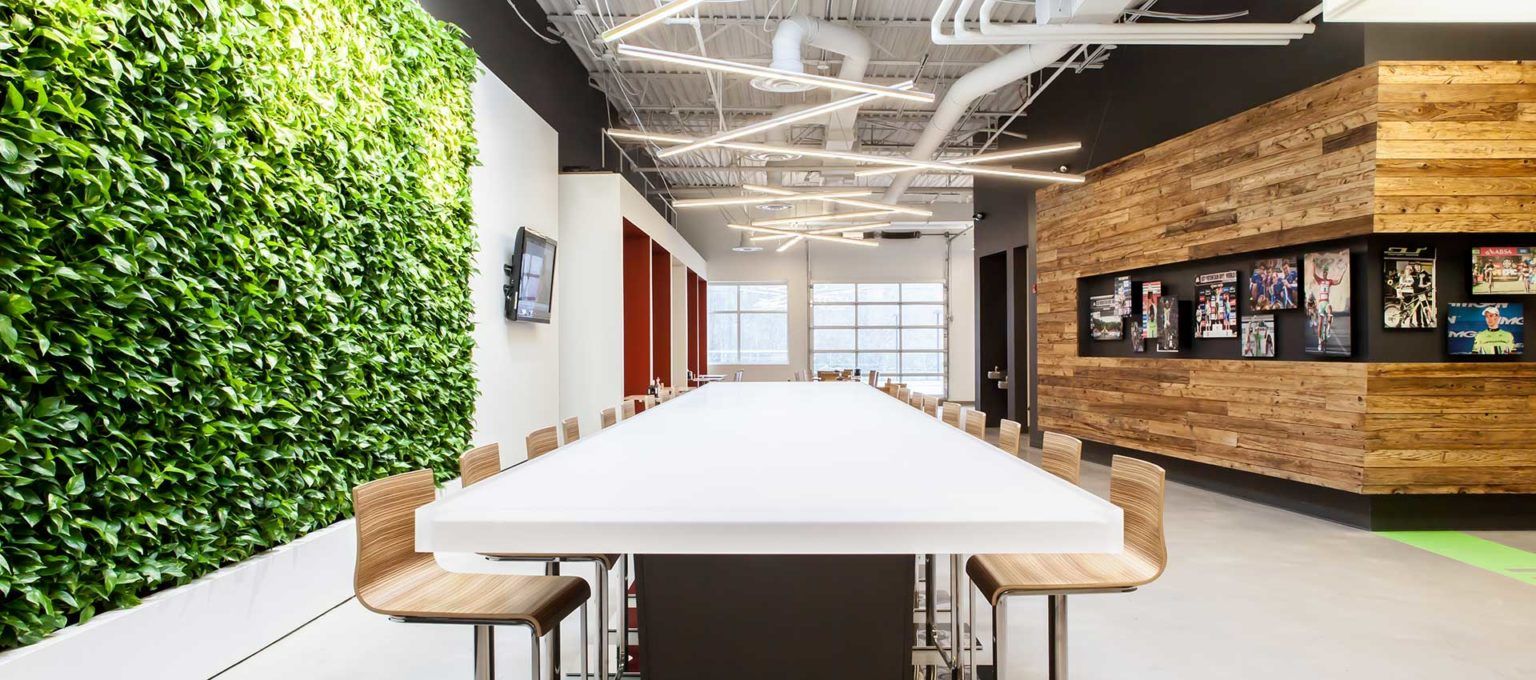
Source: teknion
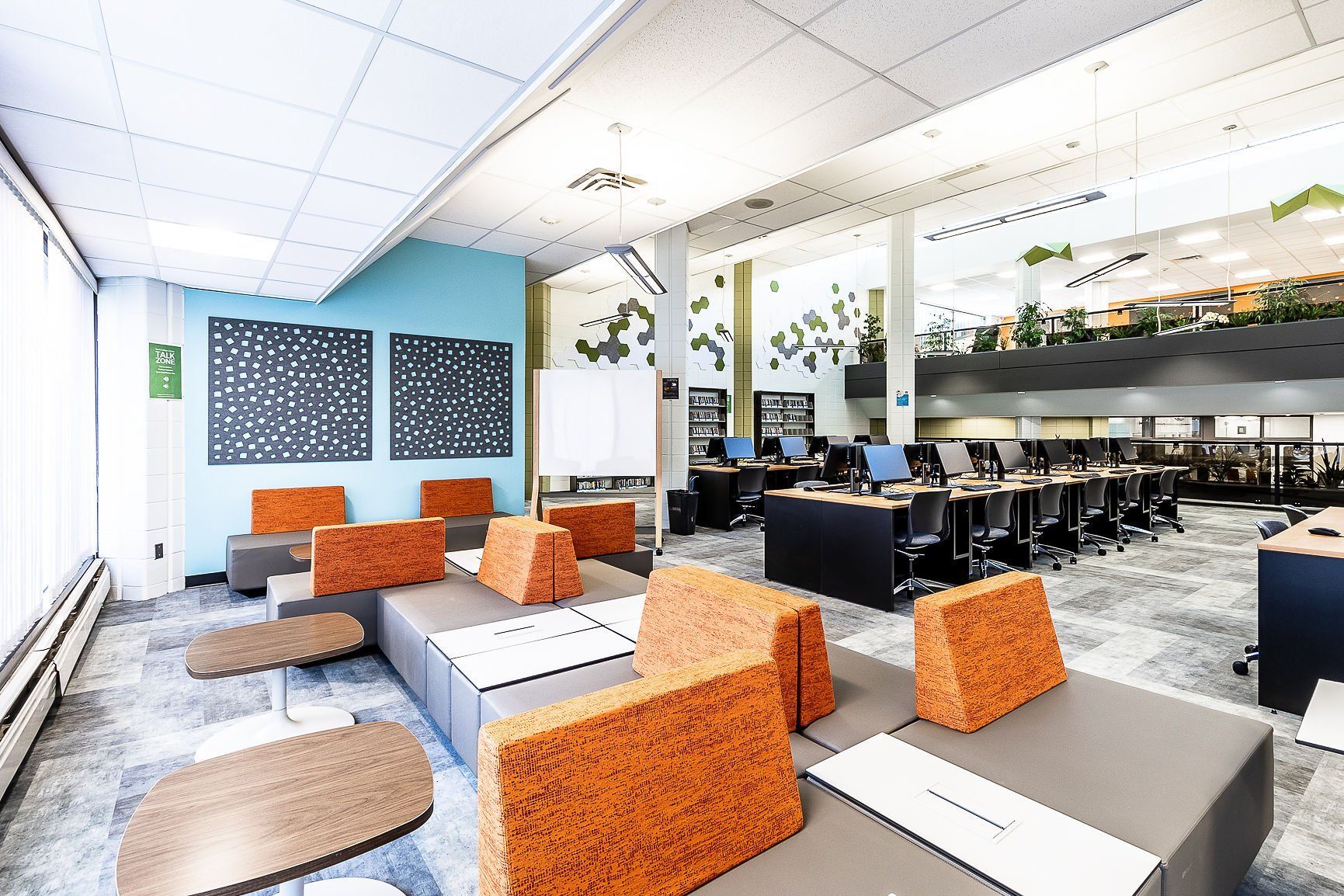
Circular Design for Workspaces
Incorporating circular design principles in interior design and construction involves creating adaptable spaces, selecting modular furniture, and using sustainable materials that minimize environmental impact and promote resource efficiency.
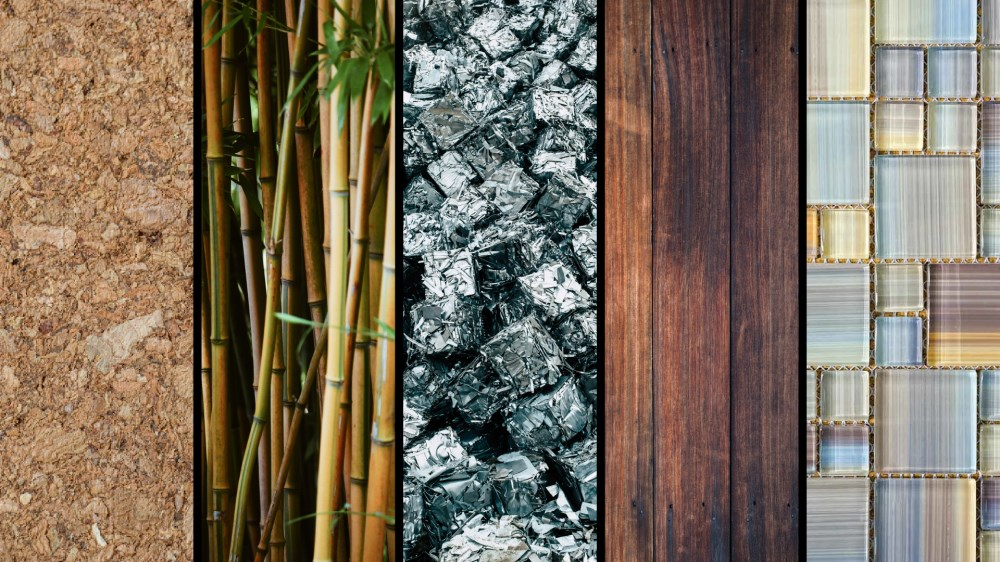

Source: swatchbox.com
1. Material Selection
- The use of recycled, recyclable, or biodegradable materials which help to conserve resources and reduce waste (e.g., reclaimed wood, recycled plastic tiles, low-VOC paints).
- Opting for durable and low-maintenance, long-lasting materials, reduces the need for frequent replacement and minimizes waste generation.
- Choosing modular materials that can be easily disassembled and reused in future fit-outs.
- Selecting certified sustainable materials (like Cradle to Cradle, FSC-certified wood)
- Use local, renewable materials that regenerate faster than they are consumed (e.g., bamboo, cork).
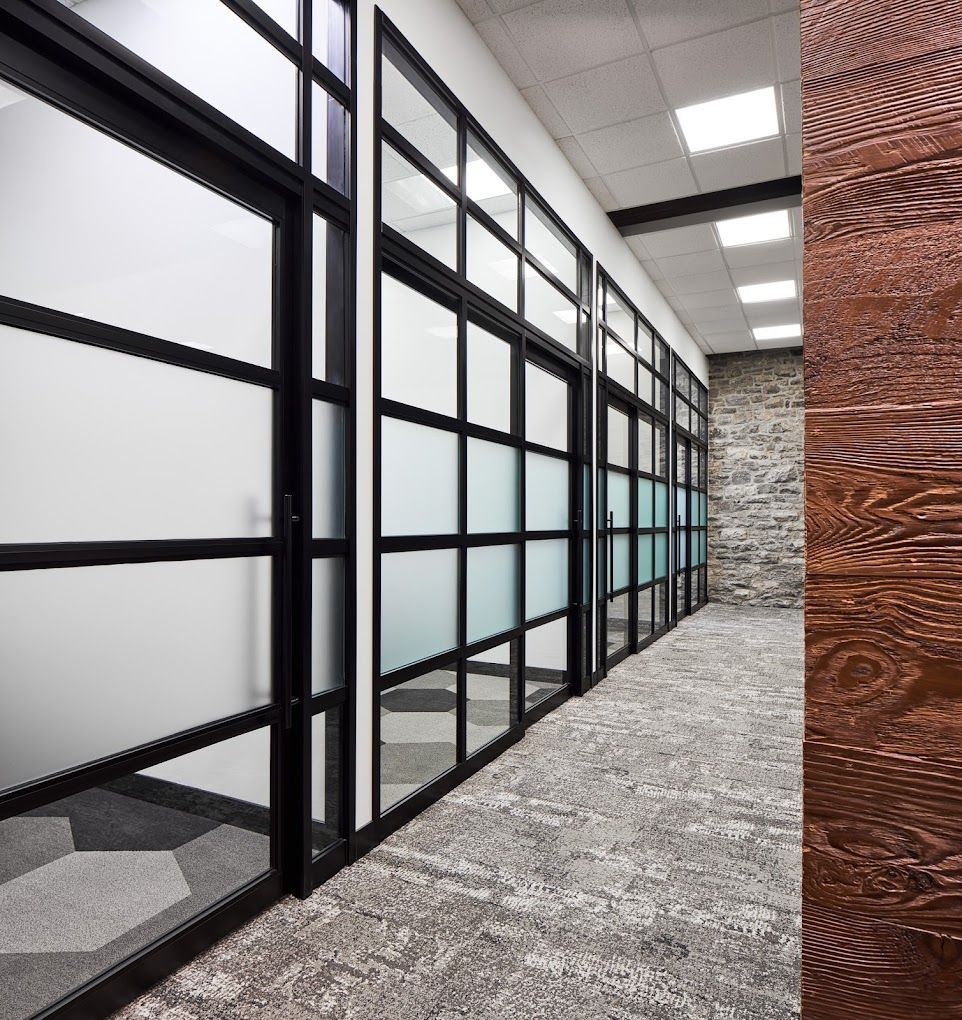

Demountable Wall Systems Source: pc350.com
2. Design for Disassembly
- Use fixtures and fittings that can be taken apart without damage.
- Modular walls, flooring systems, or ceiling panels allow for reconfiguration or reuse during office relocation or renovation.
3. Flexibility & Longevity
- Create adaptive spaces that can serve multiple functions (e.g., movable partitions, flexible furniture).
- Invest in durable, timeless design to avoid frequent renovations.

Source: Warehouse-Lighting.com
4. Furniture & Fixtures
- Opt for furniture pieces that can be easily reconfigured, allowing for customization and adaptation to different spaces and needs.
- Choose furniture designed for easy repair or updates, ensuring that individual components can be replaced or updated without discarding the entire piece.
- Prioritize furniture that can be disassembled, facilitating transportation and reducing the likelihood of damage during relocation, thereby extending its lifespan and reducing waste.
- Source second-hand or refurbished furniture or use leasing models where suppliers take back and refurbish furniture at end-of-life.

Teknion Divert Program Source: www.teknion.com/ca/about/divert-ca
5. Waste Reduction During Construction
- Implement off-site prefabrication to reduce on-site waste.
- Implement processes for efficiently handling and storing materials to minimize damage and waste. This includes ensuring materials are protected from the elements, properly stacked, and organized to prevent unnecessary waste.
- Establish a recycling program on-site to segregate and recycle construction waste, such as concrete, wood, metal, and cardboard. This not only reduces waste sent to landfills but also promotes resource efficiency.
- Encourage the reuse of materials whenever possible, either within the same project or in future projects. By reusing materials, you can conserve resources and minimize waste generation.
- Partner with construction waste management services to divert usable materials from landfill.

Source: circularpartners.ca/viking-recycling
6. End-of-Life Planning
- Incorporate take-back schemes for carpets, ceiling tiles, furniture or electronics.
- Create documentation (like a “material passport”) to support the reuse or recycling of components in the future.

Benefits of circular design for Workspaces:
- Reduced environmental impact and contribution to sustainability goals.
- Lower long-term costs through reuse and durable design.
- Improved well-being and productivity of employees from healthier indoor environments.
- Enhanced brand image as an environmentally responsible company.
- Future-proofed spaces ready to adapt to evolving business needs.
Some barriers to implementing circular design include a lack of awareness and understanding of the concept, resistance to change, limited access to sustainable materials, and the need for new business models that support circularity. Overcoming these barriers requires education, collaboration, and innovation from all stakeholders involved.
Essentially, circular design strengthens the sustainability of our world, requiring designers to use premeditative thought and design toward a circular model. By embracing circular design principles, we can minimize our environmental impact and promote a future that is prosperous and thriving for future generations.
Contact Us










